What is RFID?
Monday, March 8, 2021
Gabriel Garcia - Organizational Development Manager

Radio Frequency Identification is a technology that allows objects to be identified by radio waves in a unique way and can capture hundreds of objects at a time.
RFID tags are small, tag-like devices that can be attached to or incorporated into a product, an animal or a person.
There are different frequencies within RFID technology:
- Ultra-High Frequency (UHF): with frequencies of 860 MHz - 960 MHz and a reading range that can reach more than 12 meters..
- High Frequency (HF): with frequencies of 13.56 MHz and a reading range between 10 cm and 1m.
- Low Frequency (LW): with frequencies from 125 KHz - 134KHz, with a short reading range, about 10cm..
- Near Field Communication (NFC): with frequencies of 13.56 MHZ and a power of less than 15mA, so it has a short reading range, between 4 and 5 cm. .
HOW DOES RFID WORK?
In short, RFID systems consist of five components (See Figure 1)
RFID tags or smart tags
RFID tags come in a variety of shapes and sizes and are either "passive" or "active".
They are usually passive, which means that they do not need an integrated power supply, e.g. a battery.
Passive tags are generally made of an RFID inlay and a housing for protection against physical damage.
Inlay consists of a small silicon microchip that stores the digital identity as well as additional data and is attached to an antenna on a thin substrate such as paper or plastic film (PET).
The antenna of a passive tag receives radio waves from the reader and directs them to the microchip, where the energy is collected and used to send radio signals to the Reader.
RFID Antenna
RFID Antennas are in charge of emitting and receiving the waves that allow us to detect RFID Tags.
When an RFID tag crosses the antenna field, it is activated and emits a signal.
Antennas create different wavefields and cover different distances.
RFID Readers (Reader's)
The reader is the central part of the system. They are in charge of processing the readings made by the antennas. They have different reading modes depending on the application: inventory, multiple reading, etc.
Software
Some form of software is always necessary in an RFID system.
Depending on the application requirements, system components must be carefully chosen to enable the desired performance, accuracy and reliability.
Dependiendo de los requisitos de la aplicación, los componentes del sistema deben elegirse cuidadosamente para permitir el rendimiento, la precisión y la confiabilidad deseados.
Printers
To print the RFID tag as easily as printing a conventional tag, RFID printers/writers are required.
The printers give us the possibility to encode RFID Tags, print human readable information, barcodes and/or QR codes, simultaneously. There are models for industrial, desktop and portable environments.
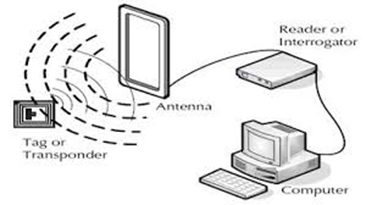
Figura 1

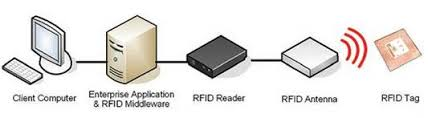
Figura 1
BENEFITS OF RFID
The ability to identify and track individual objects or containers with items without the need to have a direct view brings a lot of value to companies to control their inventories and processes.
- RFID does not require line of sight
- RFID tags can be read and re-recorded as many times as desired.
- RFID tags can be disposable or highly resistant for reuse.
- RFID tag data can be encrypted and locked.
- RFID can contain more information than other types of tags.
- RFID readers can read hundreds of tags at a time.
- RFID tags are printable.
- RFID systems can be integrated with ERP or other internal systems.
APPLICATIONS OF RFID TECHNOLOGY
Some of its most common applications are the following:
Supply Chain Management (SCM)
One of the fundamental applications that we can find is aimed at the overall improvement of the supply chain, automating, simplifying or even eliminating the work of identification and data capture that occurs at different points in the chain, thereby ensuring traceability.
This simplification results in benefits such as increased productivity and efficiency and reduced operating costs.
Industry
RFID technology can improve production times, reduce direct labor in processes that do not add value to the product and, in general, increase the overall productivity of the company.
An example is the capture of high volumes of data in procedures where it is impossible or very costly to do it manually.
To ensure complete traceability of products and simplify interactions between the various actors in the chain, RFID technology provides a global view and control of the supply chain, making it easier to manage suppliers, operations, channels and consumers, easily detecting errors and storing relevant information on each product and even on each piece (such as serial number, batch, expiration date, operator, plant or date of manufacture, among many other traceability and control variables).
Logistics
The interaction between manufacturing, distribution centers and stores are much more agile and effective with RFID technology by massively and reliably identifying the goods received, avoiding having to verify the information manually.
In addition, warehouse management is improved, as goods can be dropped off and picked up automatically.
It also reduces the time it takes to prepare, prepare and pick up orders, making it easier to detect any type of error.
With this technology we will have a global vision of the business, we will guarantee a good service, and we will see how productivity increases 20-30% more than using barcodes.
Retail
Retail is one of the sectors that has obtained the most benefits. Adhesive RFID tags placed on products help us to know at all times the exact location of each item, in addition to storing relevant information about it. This greatly simplifies inventory management, avoiding stock-outs (out of stock on the shelf).
The anti-theft/loss control system is also achieved with the use of RFID technology since a detection portal will raise the alarm in case someone tries to take a product without going through the payment point.
We can offer our customers a new shopping experience, thanks to interactive screens and mirrors that allow them to: identify and project product information; offer shopping recommendations; or request different sizes and colors, among other options.
RFID is a very useful tool to improve customer satisfaction and increase sales volume. The fashion, jewelry and cosmetics industries are some of the sectors where the technology will make a difference.
Hospitals / Pharmaceutical industry
RFID technology is a great tool for enabling the management, security and tracking of assets and people in the healthcare sector.
Some of its main functions in hospitals are: marking operating room tools that must be very precisely controlled; controlling patient and staff access to the various areas of the hospital; and storing information related to each patient's medical history to facilitate treatment and avoid confusion.
Other industries and uses of RFID technology
Food and beverages
Libraries/Documents
Sports timing
Identification and location of assets
Inventory management of any kind
Control of entries and exits of persons, objects and vehicles.
As you have seen, RFID technology offers many advantages and opportunities.
In Servibarras we have been installing and developing RFID solutions for years that adapt to all kinds of challenges.




